Securing IT Systems: A Guide to Software Authentication
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, software authentication has become an essential pillar of IT security. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, organizations must prioritize safeguarding their systems through robust authentication strategies. The effectiveness of software authentication can be the difference between a secure environment and a vulnerable system open to exploitation.
Software authentication acts as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only authorized users gain access to sensitive data and critical applications. In the realm of information technology, the consequences of inadequate authentication practices can be dire, including data breaches, financial losses, and damage to reputation. Organizations, therefore, need to understand the different types of authentication mechanisms available, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and biometric measures.
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access. This can include something they know (a password), something they have (a smartphone app), or something they are (fingerprints). Implementing MFA is one of the most effective ways to mitigate unauthorized access and enhance software authentication.
Single sign-on simplifies the user experience by allowing them to log in once and gain access to multiple applications without needing to remember multiple passwords. While SSO can improve user satisfaction, organizations must ensure that it does not act as a vulnerability in their security framework. Consistent monitoring and updates are necessary to keep authentication measures effective against evolving threats.
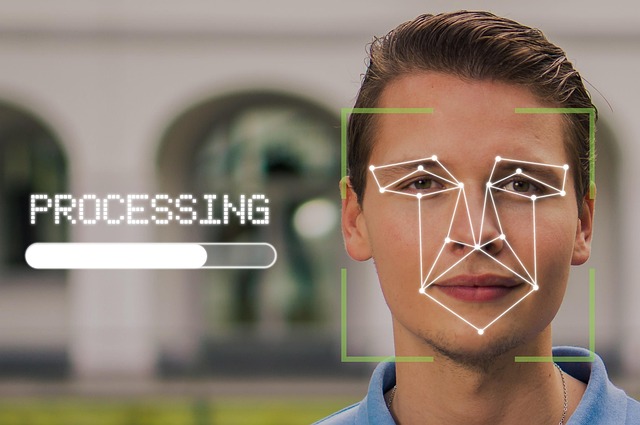
Biometric authentication is also gaining traction, utilizing unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. It offers a user-friendly and highly secure alternative that can significantly reduce the chances of unauthorized access. However, the implementation of biometric systems must consider privacy concerns and data protection regulations.
Beyond choosing the right authentication method, organizations must also foster a culture of security awareness among employees. Many data breaches occur due to user negligence, such as falling for phishing scams or using weak passwords. Continuous training and education on the importance of strong software authentication practices are essential for minimizing human error.
Moreover, integrating software authentication into software development life cycles is crucial. Developers should adopt security-first coding practices, incorporating authentication processes in the design phase rather than as an afterthought. Tools such as secure coding guidelines and regular security audits can help in creating more secure applications from the ground up.
Lastly, staying updated with the latest trends and technologies in IT security is vital. The landscape is ever-evolving, with new risks and vulnerabilities emerging regularly. Regularly updating authentication methods and being proactive about security threats will ensure that systems remain fortified against potential attacks.
In summary, software authentication is not merely a technical requirement; it is a fundamental aspect of ensuring a secure IT environment. By understanding and implementing effective authentication strategies, organizations can protect their valuable data and maintain the integrity of their systems in an era where cyber threats are ever-present.



